Note
Go to the end to download the full example code.
Calculating the radial distribution function¶
In this tutorial we will learn how to analyse (ab-initio) molecular dynamics trajectories. We will use the tool MDAnalysis to read our simulation data files and calculate the radial distribution function.
Wikipedia page on RDF: MDAnalysis documentation on RDF:
We first import our python modules
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from pathlib import Path
import MDAnalysis as mda
from MDAnalysis.analysis.rdf import InterRDF
Then we define our project path. Replace the path with your own project path
PROJECT_PATH=Path("../../../solutions/")
Next, we load our simulation output.
universe = mda.Universe(PROJECT_PATH / "dft"/ "Argon_Simulation-pos-1.xyz")
# The Universe object contains the atomic positions for each timestep. # Note that the xyz file does not contain any information on the dimensions
print(f"dimensions from xyz file {universe.dimensions}")
dimensions from xyz file None
So we must set the dimensions ourself to
box_l = 17.0742
universe.dimensions = [box_l, box_l, box_l, 90, 90, 90]
Let’s also check how many frames we’ve loaded with
print(f"loaded {len(universe.trajectory)} frames")
loaded 10001 frames
We now want to run an radial distribution analysis using InterRDF
rdf = InterRDF(universe.atoms, universe.atoms,
n_bins = 100,
range = (1.0, box_l / 2)
)
We then run the analysis with
rdf.run()
/fibus/fs3/0b/ckf7015/.local/lib/python3.11/site-packages/MDAnalysis/analysis/base.py:522: UserWarning: Reader has no dt information, set to 1.0 ps
self.times[idx] = ts.time
<MDAnalysis.analysis.rdf.InterRDF object at 0x7fee45ffb490>
Next, we plot our results
plt.plot(rdf.results.bins, rdf.results.rdf)
plt.xlabel("$r$ in A")
plt.ylabel("g(r)")
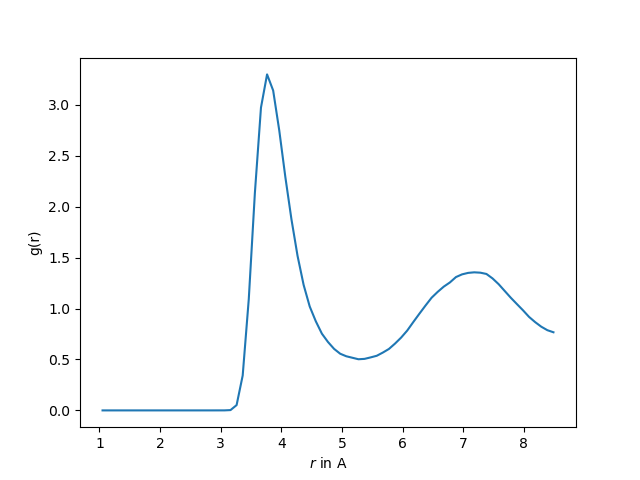
Text(42.597222222222214, 0.5, 'g(r)')
and save our figure
plt.savefig(PROJECT_PATH / "lammps" / "rdf.png", dpi=300)

Total running time of the script: (0 minutes 7.606 seconds)